Python
强类型语言:C/C++/java
弱类型语言:js/python
数据结构
-
常用数据结构 序列、集合、字典
python中的数据结构主要有:序列(字符串,元组,列表,范围,字节序列),集合,字典
序列:可迭代,元素有序,可以重复出现
集合:可迭代,元素无序,不能重复出现
字典:可迭代,可变,的K-V对
Python没有数组,可以用列表(序列)代替
-
字符串 str
索引:a[0]表示第一个,最后一个元素是a[-1],不能超出范围会有IndexError
获取长度函数len(),max返回最后一个元素,min返回第一个元素

加法和乘法:+ 把两个字符串连接起来,* 把字符串重复多次


序列切分:从序列中且分出小的序列
[start : end]:包括start,不包括end
[start : end : step]
[0 : 0 : -1]:倒置

-
元组 tuple
不可变序列,一旦创建就不能修改
a = (21,32,43,45) b = ('hello','world') c = tuple([21,32,43,54])如果只有一个元素,后面一定要加逗号隔开

元组访问和分片,左闭右开:

元组拆包:

也可以用*n表示后面剩下所有元素形成一个list列表赋值给n
也可以用下划线表示不取哪些元素

遍历元组:
for循环里的item,只是取出每个元素值
但有时需要在遍 历过程中同 获取索引,用到 enumerate() 函数可以获得元组对象,该元组对象有两个元素,一个是索引值,一个是元素值,所以(i, item) 是元组拆包过程

-
列表 list
列表具有可变性,可追加、插入、删除和替换中的元素
a = [21,32,43,45] b = ['hello','world'] c = list((21,32,43,54)) a = [10] #一个元素可以不加逗号追加元素:
追加单个元素 + append() 不能同时追加多个元素
追加另一列表 + extend()
list.append(x) list.extend(t)
插入元素:
list.insert(i,x)
替换元素:

删除元素:
list.remove(x) item = list.pop(i) #i是索引,省略则删除最后一个,返回值item是删除的元素 del list[i] #删除第i个

其他常用方法:
list.reverse() list2 = list.copy() list.clear() list.count(a) #返回x出现的次数,该方法继承自序列 list.index(x,i,j) #从i开始,j结尾,x第一次出现的索引,

注意两点:
index的i,j是左闭右开区间
index函数如果找不到是会报错的

列表推导式:
它可以将一种数据结构作为输入,经过过滤、计算等处理 最后输出另一种数据结构,根据数据结构的不同可分为列表推导式、集合推导式和字典推导式


-
集合 set
集合是可迭代、无序的、不能包含重复元素的
集合又分为可变集合(set)和不可变集合(frozenset)
创建可变集合:
创建过程中会自动去重
a = {'1','2','3'} a = set((20,10,50,40,30)) #转换之后顺序可能会改变 a = set() #创建空集合,不能用a = {},这样是一个字典返回集合元素数量:注意len是函数不是方法
len(a) √ a.len() ×修改可变集合
myset.add(x) myset.remove(x) #删除,如果元素不存在,报错 myset,discard(x)#删除,如果元素不存在,不报错 myset.pop() #删除任意一个元素,返回值是删除的元素 myset.clear()
遍历集合:
集合是无序的,不能通过下标访问单个元素
第二个循环中的i不是索引,只是遍历集合的次数

不可变集合的创建:
set = frozenset({'1','2','3'})
不可变集合不能被修改,修改时会报错
集合推导式:

-
字典 dict
创建字典:
mydict = {} mydict = {key1:value1 , key2:value2 , key3:value3} mydict = dict(list) mydict = dict(tuple) mydic = dict(zip([1,2,3],['z','c','y'])) mydic = dict(key=value , key=value , key=value) #仅适用于字符串键

修改字典:添加、替换、删除
mydict[key]=value #添加和替换 del mydict[key] mydict.pop(key) mydict.pop(key,value) #删除key对应的键值对,return value #如果键值对不匹配,且健不存在,就不删除 mydict.popitem() #删除任意键值对,返回键值对元组

访问字典:
mydict.get(key,value) #返回这个key对应的value,如果不存在返回value mydict.items() #返回字典的所有键值对 dict_items([list]) mydict.keys() #返回所有keys dict_keys([list]) mydict.values() #返回所有的values dict_values([list]) in/not in #只适用于键

遍历字典:
遍历过程可以只遍历值视图,也可以只遍历键视图,也可以同时遍历

字典推导式:
注意输入结构不能直接使用字典,因为字典不是序列,可以通过字典的 item() 方法返回字典中键值对序列

函数
-
定义函数
定义函数:
def funcname(type value): ... return value函数名需要符合标识符命名规范
多个参数列表之间可以用逗号分隔,也可以没有参数
如果函数有返回数据,就需要在函数体最后使用return语句将数据返回
如果没有返回数据,则函数体中可以使用return None或省略return语句
-
可变参数
可变参数:
中函数的参数个数可以变化,它可接受不确定数量的参数 ,这种参数称为可变参数
*可变参数在函数中被组装成为元组


**可变参数在函数中被组装成为字典


面向对象
-
类和对象
定义类:
class Animal(object): ......构造函数:
用来创建和初始化 实例变量
self必须是第一个参数,创建对象的时候调用
参数列表必须和__ init __()的参数列表匹配
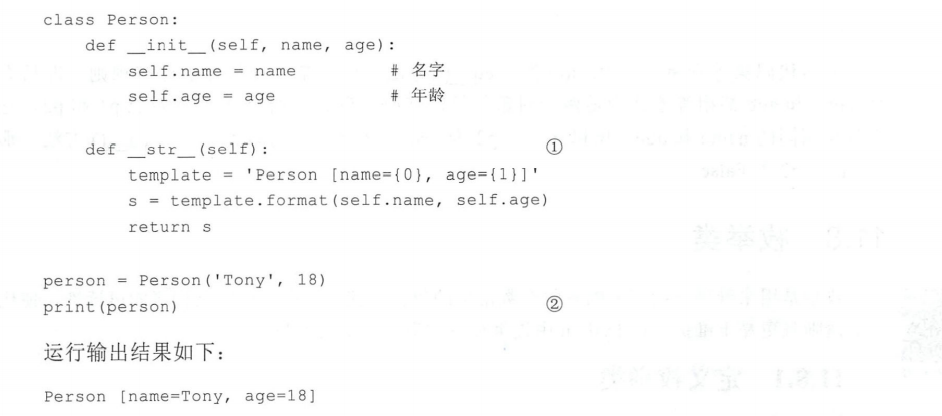
def __init__(self,width,height): self.width = width self.height = height创建和使用对象:
animal = Animal()打印对象:
print(animal) #<__main__ .Animal object at Ox0000024Al8CB90FO>print 函数调用了对象的__ str __ () 方法输出字符串信息,它会返回有关该对象的描述信息 ,由于本例中 Animal 的__ str __()方法是默认实现的,所以会返回这些难懂的信息
实例变量:
存储描述对象的状态特征的值
在内部通过self.变量名访问,在外部通过 对象名.变量名 访问


类变量:
是所有实例或对象共有变量
创建类变量与实例变量不同,类变量要在方法之外定义
通过 类名.类变量 的形式访问

实例方法:
普通方法,属于某个实例或对象特有的
第一个参数必须是self

类方法:
类方法不需要与实例绑定,需要与类绑定
定义时它的第一个参数不是 self,而是类的 type 实例 cls
使用装饰器 @classmethod
在类方法中可以访问他的类变量和类方法,cls. interest_rate

静态方法:
使用了@staticmethod 装饰器
如果定义的方法既不想与实例绑定,也不想与类绑定,只是想把类作为它的命名空间
调用静态方法与调用类方法类似都 类名.方法名 实现, 但也可以用实例调用

-
封装性
私有变量:
默认情况 Python 中的变量是公有的,可以在类的外部访问它们 。如果想让它们成为私有变量,可以在变量前加上双下划线 __

私有方法:
私有方法与私有变量的封装是类似的,只要在方法前加上双下划线 __ 就是私有方法了
私有方法可以在类的内部访问,不能再类的外部访问

定义属性:
在严格意义上的面向对象设计中,是不应该有公有实例成员变量,这些实例成员变量应该被设计为私有,然后通过公有 setter getter 访问器访问


访问器形式在封装时比较麻烦,python中提供了属性property
定义时可以使用@property 修饰getter,和 @属性名.setter 修饰setter

-
继承性
子类继承父类所有的成员变量和方法,除了私有部分
构造函数:
子类的构造函数中,不会自动调用父类构造函数,需要显式编写

重写方法override:
子类方法名和父类的方法名相同,参数列表相同

多继承:
一个子类可以有多个父类
当子类实例调用一个方法时,先从子类中查找,如果没有找到则查找父类。父类的查找顺序是按照子类声明的父类列表 从左到右 查找 ,如果没有找到再找父类的父类


-
多态性
发生多态要有两个前提条件
1.继承—多态发生一定是子类和父类之间
2.重写一子类重写了父类的方法

类型检查:
isinstance(obj, classinfo) 检查obj 实例是否由 classinfo 类或 classinfo 子类所创建的实例

-
object 根类
__str__() #返回对象名和内存地址等信息 __eq__(other) #指示其他某个对象是否与此对象相等 == #内容比较符重写str
重写eq

-
枚举类
管理一组有限个常量的集合
枚举类不能调用构造方法
枚举实例 value 属性是返回枚举值,name 属性返回枚举名。
import enum class enumname(enum.Enum): list....

限制枚举类:
为了使枚举类常量成员只能使用整数类型,可以使用 enum.IntEnum 作为枚举父类
@enum.unique 装饰器,保证成员取值不同

使用枚举类:



异常处理
-
异常类继承层次
Python 中异常根类是 BaseExcption
BaseException 的子类很多,其中 Exception 是非系统退出的异常,它包含了很多常用异常。如果自定义异常需要继承 Exception 及其子类,不要直接继承 BaseException


-
常见异常
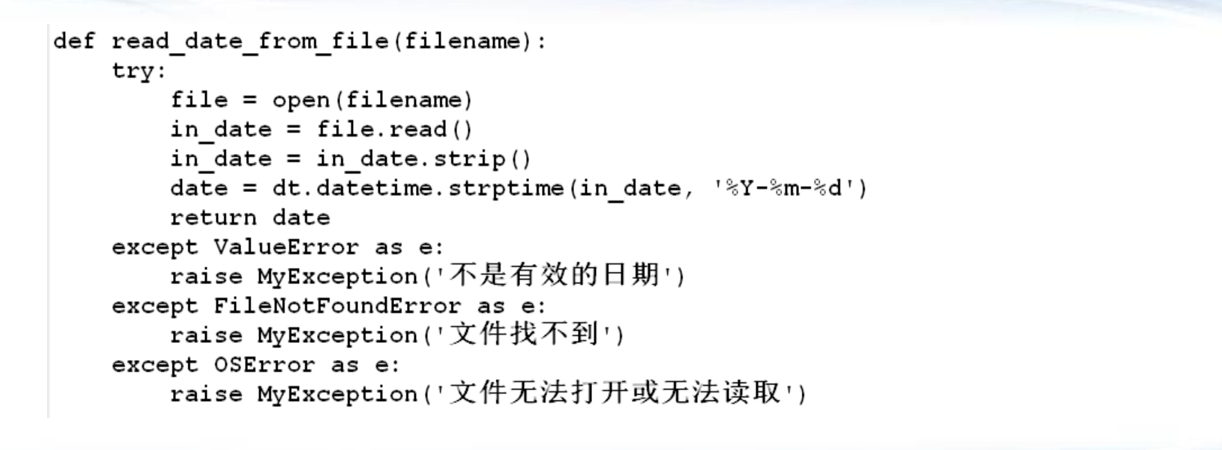
AttributeError:试图访问某个类中不存在的成员(包括成员变量、属性和成员方法)
OSError:操作系统相关异常,例如“未找到文件”或“磁盘己满”,FileNotFoundError 属于 OSError
IndexError:是访问序列元素时,下标引超出取值范围所引发的异常
KeyError:试图访问字典里不存在的键

NameError:视图访问不存在的变量

TypeError:试图传入变量类型与要求的不符合 5/‘2’

ValueError:传入无效参数

-
捕获异常
try: #可能会抛出异常的语句 except xxxError as e: #处理异常
print(e) 指令可以打印异常对象,输出异常描述信息
多except代码块:如果抛出异常类型有多种,在多 except 代码情况下,当一 except 码块捕获到一个异常时,except 块就不再进行匹配。
try: #可能会抛出异常的语句 except Type1Error as e: #处理异常 except Type2Error as e: #处理异常 ... except TypenError as e: #处理异常注意: 捕获异常类之间存在父子关系,捕获异常顺序 except 代码块的顺序有关

如果改成这样,那么FileNotFound Error 异常处理永远不会执行,OSError是FileNotFoundError的父类,而 ValueError 异常与 OSError FileNotFoundError异常没有父子关系,捕获ValueError异常位置可随意放置
try-except语句嵌套:
时如果内层抛异常首先由内 except 进行捕获,如果捕获不到, 由外

多重异常捕获: Python 中可以把这些异常放到一个元组中,这就是多重异常捕获

为什么不写成(ValueError, FileNotFoundError, OSError),因为 FileNotFoundError 属于 OSError 异常,OSError 异常可以捕获它的所有子类异常
异常堆栈跟踪:
import traceback traceback.print_exc(limit,file,chain=True)释放资源:
finally:无论 try 正常结束还是 except 异常结束都会执行 finally 码块
else:在程序正常结束时执行的代码块

with as:代码块自动资源管理,可以代替finally,as 后面声明一个资源变量 with as 代码块结束之后自动释放资源
-
自定义异常
继承Exception类或者子类
提供一个字符串参数的构造函数

显示抛出异常:
使用raise语句主动抛出异常
显式抛出异常的目的有很多,例如不想某些异常传给上层调用者,可以捕获之后重新显式抛出另外一种异常给调用者
常用模块
-
Math
math
import math math.ceil(a) math.floor(a) math.round(a) #四舍五入 math.log(a,base) #取对数 math.log(8,2)=3 math.sqrt(a) #平方根 math.pow(a,b) #math.pow(2,3)=8 math.degrees(a) #将弧度a转换为角度 math.radians(a) #将将角度a转换为弧度 math.sin(a) #返回弧度a的三角正弦 a = math.radians(45/math.pi) math.cos(a) #返回弧度a的三角余弦 -
Random
random
import random random.random() #0.0<=x<1.0 的随机浮点数 random.randrange(step) #0<=x<stop 随机整数 random.randrange(strat,stop,step) #start<=x<stop 随机整数 random.randint(a,b) #a<=x<b 随机整数 -
Datetime
datetime
import datetime #datetime datetime.datetime(y,m,d) #创建datetime对象 datetime.datetime.today() datetime.datetime.now(tz=None) datetime.datetime.utcnow() #格林威治时间 datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp,tz=None) #UNIX时间戳是自1970年1月1日00:00:00以来的秒数,返回与UNIX时间戳对应的本地日期和时间 datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(timestamp,tz=None) #date datetime.date(y,m,d) #创建date对象,d=datetime.date(2021,7,12) datetime.date.today() #返回今天 datetime.date.fromtimedtamp(99999999.999)#根据时间戳返回日期 #time datetime.time(h,m,s,micro) #创建time对象 0<=micro<1000000用日期时间计算
import datetime #timedelta datetime.timedelta(days,sec,microsec,millisec,minute,hr,weeks)
日期格式化 strptime



-
String
字符串
in/not in isalpha() #True, 如果字符串只包含字母,并且非空 isalnum() #True,如果字符串只包含数字字母,并且非空 isdecimal() #True,如果字符串只包含数字,并且非空 startswith(a) endsWith(a) string=char.join(list) list=string.split(char) str.center() #居中 str.ljust() #左对齐 str.rjust() #右对齐 strip(), lstrip(), rstrip() #去除字符串两头的空格 index() #找不到报异常 find() #找不到不报异常 replace(str1, str2) #s.replace('ab','cd')

strip():
当参数为空时,默认删除空白符,包括’\n’, ‘\r’, ‘\t’, ’ '
这里的删除序列是只要边(开头或结尾)上的字符在删除序列内,就删除掉,不考虑顺序


-
Matplotlib
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H"] y = [150, 85.2, 65.2, 85, 45, 120, 51, 64] plt.xlabel("X") plt.ylabel("Y") plt.title('Picture Name') plt.bar( x=x, # Matplotlib自动将非数值变量转化为x轴坐标 height=y, # 柱子高度,y轴坐标 width=0.6, # 柱子宽度,默认0.8,两根柱子中心的距离默认为1.0 align="center", # 柱子的对齐方式,'center' or 'edge' color="grey", # 柱子颜色 edgecolor="red", # 柱子边框的颜色 linewidth=2.0 # 柱子边框线的大小 ) plt.style.use('')选择风格 https://blog.csdn.net/viviliving/article/details/107690844 plt.show()

柱状图

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置表格的风格
plt.style.use("seaborn-dark")
# 课程时间线
# 方法一;横坐标精确到每分钟
# x = ["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10",
# "11", "12", "13", "14", "15", "16", "17", "18", "19", "20",
# "21", "22", "23", "24", "25", "26", "27", "28", "29", "30",
# "31", "32", "33", "34", "35", "36", "37", "38", "39", "40"]
# 方法二:横坐标精确度为 0 10 20 40
x = np.arange(41)
# 黑色柱状图
black_part = [0, 0, 0, 85, 85, 85, 0, 0, 60, 60,
0, 0, 85, 85, 0, 0, 45, 45, 45, 45,
0, 0, 0, 0, 60, 60, 60, 0, 0, 60,
60, 0, 0, 0, 45, 45, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
# 底下的彩色横线
red_part = [ -0, -0, -0, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10,
-10, -10, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0,
-0, -0, -0, -0, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -0,
-0, -0, -0, -0, -10, -10, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0 ]
green_part = [ -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -10, -10, -0, -0,
-0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0,
-0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -10,
-10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
blue_part = [-0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -10, -10, -0, -0,
-0, -0, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10,
-0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0, -0,
-0, -0, -0, -0, -10, -10, -10, -10, -0, -0, 0 ]
timeline = [-10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10,
-10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10,
-10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10,
-10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, -10, 0]
teacher_disturb = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -20, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -20, 0, 0, 0, 0]
# 黑色柱状图
plt.bar(x=x, height=black_part, color='dimgray', bottom=0, label="timelin", width=1, align='edge')
# 时间线上的
plt.bar(x=x, height=timeline, color="linen", label="timeline", width=1, align='edge')
plt.bar(x=x, height=red_part, color="lightcoral", label="red_part", width=1, align='edge')
plt.bar(x=x, height=green_part, color="aquamarine", label="green_part", width=1, align='edge')
plt.bar(x=x, height=blue_part, color="cornflowerblue", label="green_part", width=1, align='edge')
#教师干扰
plt.bar(x=x, height=teacher_disturb, color="dimgray", label="teacher", width=0.2, align='edge')
# 柱状图的标题设置
plt.title("My table", fontsize=12)
plt.xlabel("Timeline", fontsize=12)
plt.show()
文件管理
-
打开文件
统计所有py文件有多少行代码
打开文件
Open(file, mode=‘r’, buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True, opener=None) #file 文件名 可以是相对路径 可以是绝对路径 #mode r只读 w写入会覆盖 x独占创建 a追加 b二进制 t文本 +更新 #buffer 0关闭缓冲区 -1自动设置缓冲区 #encoding 通常是utf-8, gbk, ansi等 #errors 表示编码出错时的动作 #newline 换行模式 #closefd #opener
f_name=r'D:\mytest\test.txt' f = open(f_name,'w+') f.write('world') f = open(f_name,'r+') f.write('hello') f = open(f_name,'a') f.write('w') with open(f_name,'r') as f: content=f.read() print(content) -
关闭文件
关闭文件
当使 open()函数打开文件后,若不再使用文件应该调用文件对象的 close()方法关闭文件。文件的操作往往会抛出异常,为了保证文件操作无论正常结束还是异常结束都能够关闭文件,调用 close()方法应该放在异常处理 finally 代码块中。但更推荐使用 with as 代码块进行自动资源管理

with as打开文件,open() 返回文件对象赋值给变量,f.read()是读取文件,最后在 with 代码结束时关闭文件
-
文件读写
文本文件读写
Read(size=-1) #读取size个字符,-1表示不限,下同 Readline(size=-1) #读取单行字符 Readlines(hint=-1)#读取每一行到一个列表中,hint表示行数 Write(s) #将s写入到文件中 Writelines(lines) #向文件写入一个列表,不添加分隔符 Flush() #刷新缓存区,写入到文件中文本文件读取

二进制文件读取

-
OS 模块
os模块
如果通过Python程序管理文件或目录,如删除文件、修改文件名、创建目录、删除目录和遍历目录等,可以通过 Python OS 模块实现
import os os.rename(src, dst)#将src文件名字修改为dst os.remove(path) #删除文件,如果删除目录,引发异常 OSError os.mkdir(path) #创建新目录,如果存在,引发异常 FileExistsError os.rmdir(path) #删除目录,如果目录非空,引发异常 OSError os.walk(top) #遍历top所有子目录,自顶向下,返回一个三元组 (目录路径,目录名列表,文件名列表) os.listdir(dir) #列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录 #两个常用属性 os.curdir #当前目录 os.pardir #上一级目录import os f_name=r'D:\mytest\test.txt' copy_f_name=r'D:\mytest\copy.txt' #如果文件夹没有,会自己创建copy.txt文件 with open(f_name,'r') as f: content=f.read() with open(copy_f_name,'w') as c: c.write(content) try: os.rename(copy_f_name,r'D:\mytest\copy2.txt') except OSError e: os.remove(r'D:\mytest\copy2.txt') print(os.listdir(os.curdir)) print(os.listdir(os.pardir)) #打印的是pythonProject文件夹目录 结果 ['.idea', 'main.py', 'my.py', 'text.txt'] ['pythonProject', 'test']
import os try: os.mkdir('subdir') except OSError: os.rmdir('subdir') for item in os.walk('.'): print(item)os.path
import os os.path.abspath(path): 返回path绝对路径 os.path.basename(path): 返回path的基础部分 os.path.dirname(path): 返回path中的目录部分 os.path.exists(path):判断path是否存在 os.path.isfile(path): 判断path是否是文件 os.path.isdir(path): 判断path是否是目录 os.path.getatime(path): 返回文件最后访问时间戳 os.path.getmtime(path): 返回文件最后修改时间戳 os.path.getctime(path): 返回文件创建时间戳 os.path.getsize(path): 返回文件大小,以字节为单位

例题:找出文件夹下所有的png文件并将后缀改为jpg
import os import string dirName = "D:your path\\" #最后要加双斜杠,不然会报错 li=os.listdir(dirName) for filename in li: newname = filename newname = newname.split(".") if newname[-1]=="png": newname[-1]="jpg" newname = str.join(".",newname) #这里要用str.join filename = dirName+filename newname = dirName+newname os.rename(filename,newname) print(newname,"updated successfully")
杂项
-
if __ name __ == ‘__ main __’
当我们把模块A中的代码在模块B中进行import A时,只要B模块代码运行到该import语句,模块A的代码会被执行,当你要导入某个模块,但又不想该模块的部分代码被直接执行,那就可以这一部分代码放在 “if __ name __ ==’ __ main __’:”内部
import sys def main(): print("hello") if __name__ == '__main__': sys.exit(main()) #the result is hello #退出时执行main -
input
Python3的input返回都是字符串
多个数据可将字符串按照规则分开
a,b,c = input().split('.') -
对象的可变性和拷贝
可变对象mutable:列表/集合/字典,自定义对象等,可以在原来地址空间进行修改
不可变对象immutable:字符串,数字int,元组等,不可以在原地址修改,而是要另辟内存空间
>>>list=[2,2,3] >>> id(list) 2075076860608 >>> list[0]=1 >>> id(list) 2075076860608 #地址空间未改变 >>> a=0 >>> id(a) 2075040573712 >>> a=1 >>> id(a) 2075040573744 #地址空间改变了列表的更新
>>> a = [1,2,3] >>> b = a >>> id(b) 1633541432192 >>> id(a) 1633541432192 >>> a = [1,2,3,4] >>> b [1, 2, 3] >>> id(a) 1633538994304 >>> a = [1,2,3] >>> b = a >>> a.append(4) >>> b [1, 2, 3, 4] #append是自身更新地址不会改变
**浅拷贝(copy):**拷贝父对象,不会拷贝对象的内部的子对象
a 和 b 是一个独立的对象,但他们的子对象还是指向统一对象(是引用)
深拷贝(deepcopy): copy 模块的 deepcopy 方法,完全拷贝了父对象及其子对象
a 和 b 完全拷贝了父对象及其子对象,两者是完全独立的

>>> import copy >>> origin = [1, 2, [3, 4]] #origin 里边有三个元素:1, 2,[3, 4] >>> cop1 = copy.copy(origin) >>> cop2 = copy.deepcopy(origin) >>> cop1 == cop2 True >>> cop1 is cop2 False #cop1 和 cop2 看上去相同,但已不再是同一个object >>> origin[2][0] = "hey!" >>> origin [1, 2, ['hey!', 4]] >>> cop1 [1, 2, ['hey!', 4]] >>> cop2 [1, 2, [3, 4]] #把origin内的子list [3, 4] 改掉了一个元素,观察 cop1 和 cop2is 比较两个对象内存地址是否相等
== 比较内容是否相等,调用__ eq() __法
#没有子对象的list test >>> import copy >>> ori=[1,2,3] >>> cp1=copy.copy(ori) >>> cp2=copy.deepcopy(ori) >>> cp1==cp2 True >>> cp1==ori True >>> cp2==ori True >>> cp1 is cp2 False >>> cp1 is ori False #改变一些值,如果不是数组里的,浅拷贝也不会改变值 >>> ori[0]=0 >>> ori [0, 2, 3] >>> cp1 [1, 2, 3] >>> cp2 [1, 2, 3]继续理解
import copy a = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b']] #原始对象 b = a #赋值,传对象的引用 c = copy.copy(a) #对象拷贝,浅拷贝 d = copy.deepcopy(a) #对象拷贝,深拷贝 a.append(5) #修改对象a a[4].append('c') #修改对象a中的['a', 'b']数组对象 #result ('a = ', [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c'], 5]) ('b = ', [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c'], 5]) ('c = ', [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c']]) ('d = ', [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b']]) -
列表的排序
b = [5,4,6,3,1] b = sorted(b) print(b) # 1,3,4,5,6 a = [('x', 0.56), ('a', 1.28), ('c', 2.36), ('s', 5.02), ('h', 20)] a = sorted(a, key=lambda x: x[0]) print(a) class Student(object): def __init__(self, name, score): self.name = name self.score = score L = [Student('Tim', 99), Student('Bob', 88), Student('Alice', 97)] L.sort(key=lambda x: x.score, reverse=True) for x in L: print(x.name + ',' + str(x.score)) -
错题
